Implantology is the branch of dentistry that replaces missing teeth with artificial tooth roots (dental implants). Implants are titanium screws placed in the jawbone, on which aesthetic and functional dental prostheses are fixed. Missing teeth can negatively affect chewing and speech functions, as well as aesthetically damage the self-confidence of individuals. Implant treatment provides both aesthetic and functional satisfactory results by offering a permanent and natural-looking solution to replace missing teeth.
What is a Dental Implant?
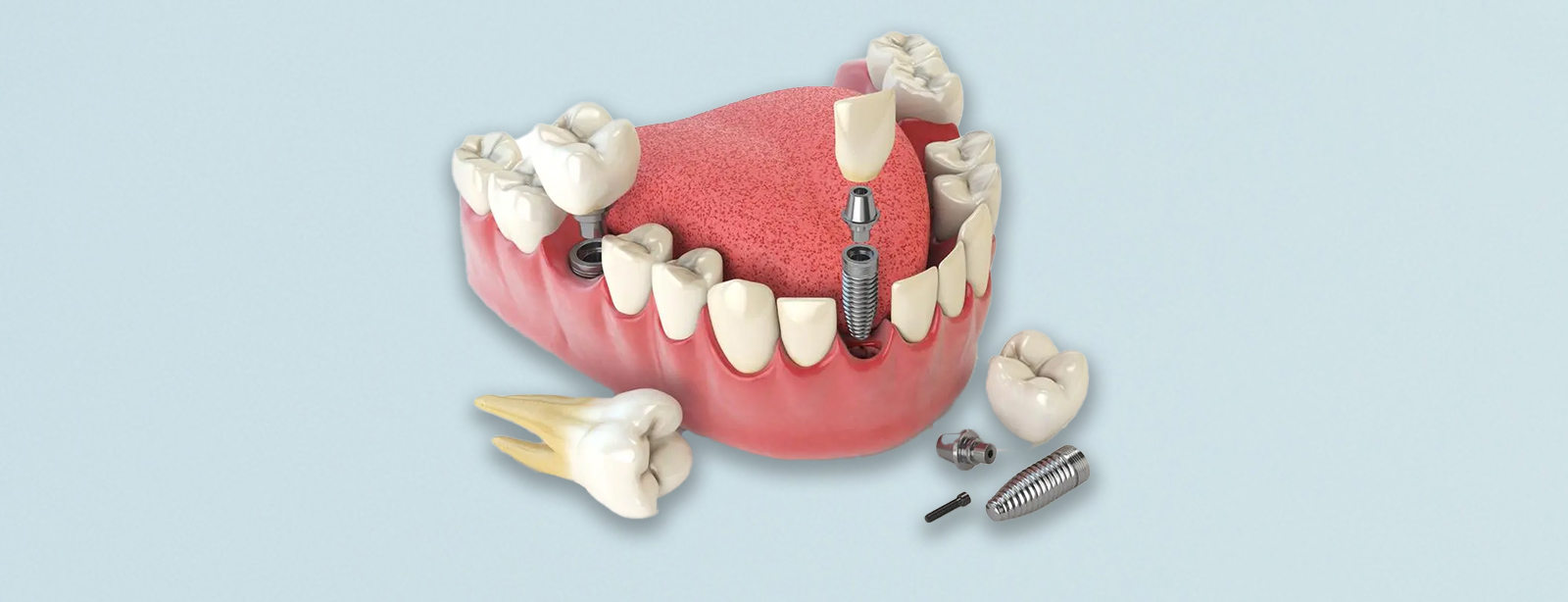
A dental implant is a screw system that functions as a tooth root and is placed in the jawbone. Implants are usually made of titanium because titanium is biologically compatible with body tissues and easily fuses with the jawbone. Once the implant is placed, it integrates with the jawbone (osseointegration) and thus fixed dentures can be placed on the implant. Implants can be used in cases where a single tooth is missing, as well as in patients with multiple tooth loss.
In Which Situations Is Implantology Applied?
Dental implants are a treatment method applied to patients with various tooth losses. Implant treatment may be preferred in the following cases:
Single Tooth Loss: When a single tooth is lost, the missing tooth is completed by placing an implant in the empty tooth socket.
Multiple Tooth Loss: In case of loss of more than one tooth, more than one implant can be placed to replace the missing teeth.
Complete Toothlessness: In individuals with no teeth left in the mouth, a fixed prosthesis can be made by placing more than one implant in the jawbone. In this case, treatment methods such as “All-on-4” or “All-on-6” can be applied.
How is Dental Implant Treatment Performed?
Implant treatment usually consists of several stages and a customized treatment plan is created for each patient:
Examination and Planning: In the first stage, your dentist will use imaging methods such as panoramic x-rays or 3D tomography to evaluate the structure of your jawbone. These examinations are done to determine whether the jawbone can support the implants and the most suitable implant placement points.
Implant Placement: Under local anesthesia, the dentist places the implant in the jawbone with a small surgical procedure. It usually takes 3-6 months for the implant to integrate with the jawbone (osseointegration). In this process, healthy bone tissue forms around the implant and the implant is firmly fused to the jawbone.
Temporary Prosthesis: After implant placement, a temporary prosthesis can be used to meet the patient’s aesthetic and functional needs. This temporary prosthesis helps the patient to continue his/her daily life comfortably during the healing process.
Permanent Prosthesis: After the implant has fully fused with the bone, the permanent prosthesis (crown, bridge or removable prosthesis) is fixed on the implant. At this stage, the prosthesis is specially prepared for the patient according to the measurements taken by your dentist and provides an aesthetically very similar appearance to natural teeth.
Advantages of Implant Treatment
Implant treatment is one of the most advanced methods offering permanent solutions to replace missing teeth. The main advantages of this treatment are as follows:
Natural Appearance and Function: Implants successfully restore chewing, speaking and aesthetic functions by replacing natural teeth.
Permanent Solution: If well cared for, implants can be used for a lifetime. It is a much longer lasting solution than other prostheses.
Jawbone Protection: After tooth loss, the jawbone may erode over time. Since implants are placed in the jawbone, they prevent bone loss and help preserve the jaw structure.
No Damage to Neighboring Teeth: In traditional bridge treatment, neighboring teeth need to be reduced to complete the missing tooth. However, implant treatment does not require this procedure and neighboring teeth are not damaged.
Better Comfort and Confidence: Since implants are fixed, the discomforts experienced with removable prostheses (moving, falling, difficulty in speaking) are not seen in implant treatment. This provides patients with more comfort and self-confidence.
Who is Implantology Suitable for?
Implant treatment is generally suitable for individuals whose jawbone has sufficient thickness and height and who are in good general health. However, the following conditions may affect the applicability of the treatment:
Insufficient Jawbone: In patients with insufficient jawbone, additional treatment methods such as bone grafting (adding bone powder) may be used.
General Health Status: Factors such as diabetes, bone diseases or smoking can affect the success of implant treatment. Therefore, the general health status of the patient is taken into consideration before treatment.
Gum Diseases: In patients with gum problems, these diseases should be treated first
